China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News: This article dives into China’s incredible manufacturing dominance, exploring its historical rise, key sectors, global impact, and the challenges it faces. We’ll examine how China became a global manufacturing hub, analyzing its economic policies, technological advancements, and its crucial role in global supply chains. Get ready for a fascinating look at the engine driving much of the world’s production.
We’ll cover everything from the historical context of China’s manufacturing boom to the current challenges posed by rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and increasing global competition. We’ll also look at how technological advancements, such as automation and AI, are reshaping the landscape and what strategies China might employ to maintain its leading position. The impact of geopolitical factors and the importance of sustainable and ethical manufacturing practices will also be key discussion points.
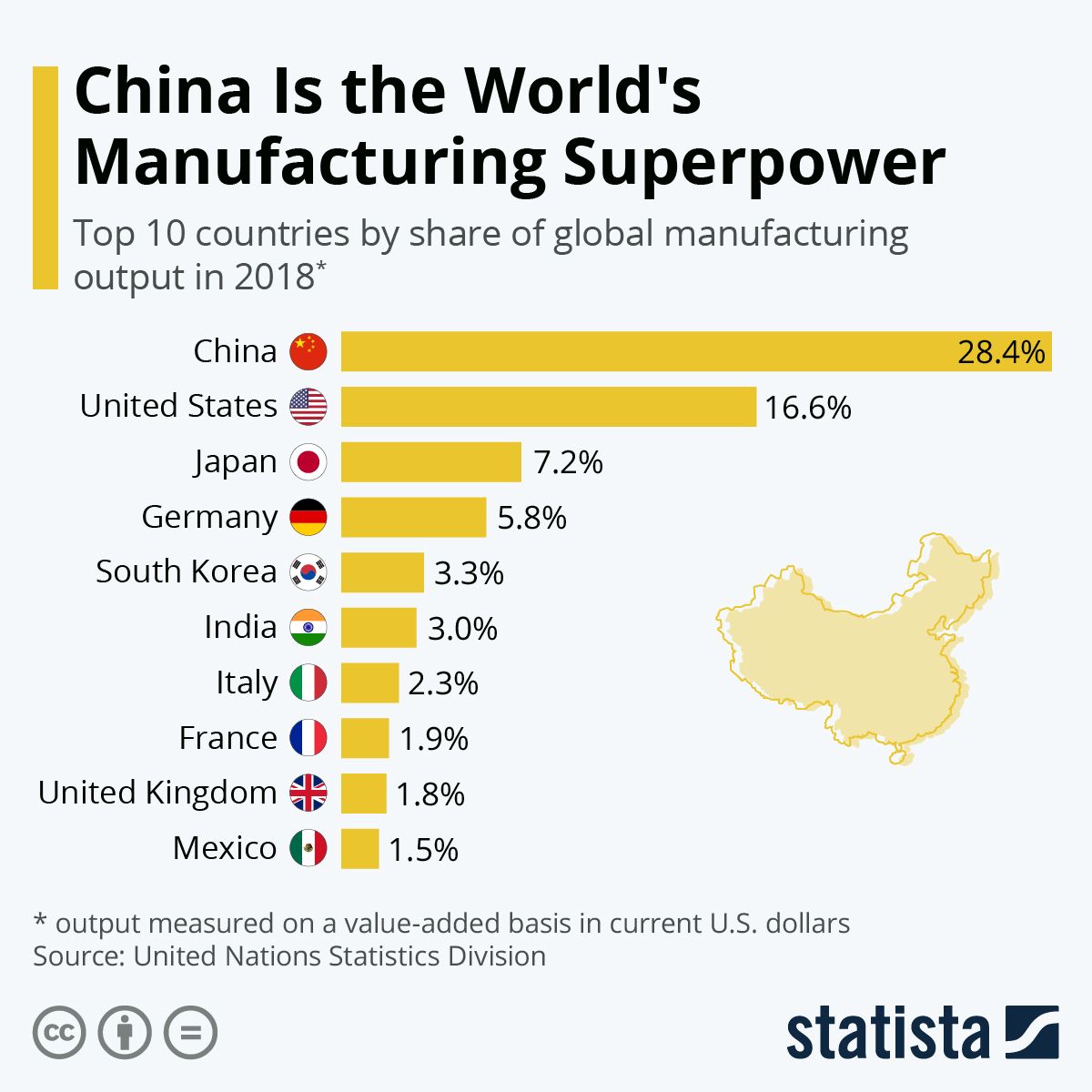
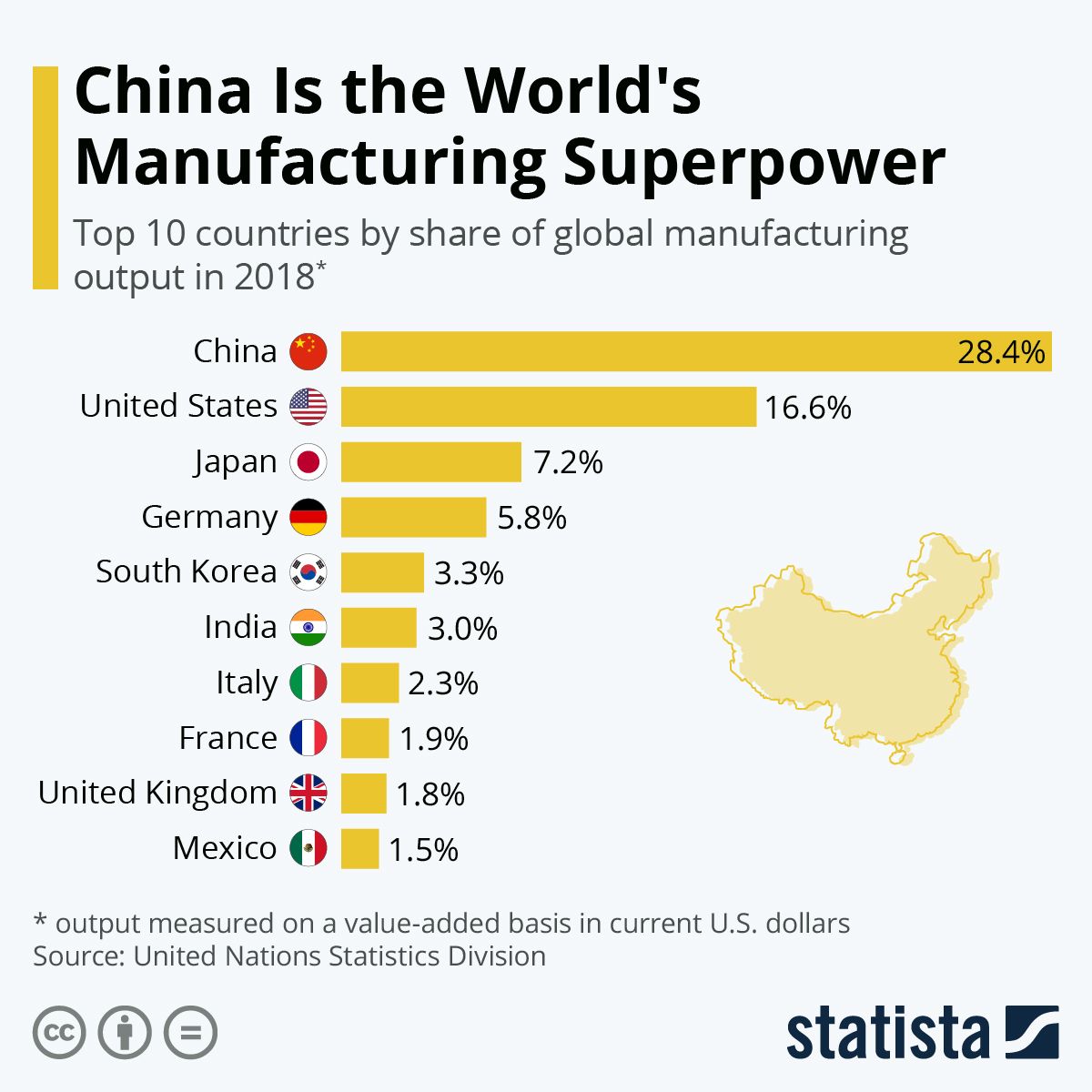
China’s Manufacturing Dominance

China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy just a few decades ago, China has become the global factory, dominating numerous industries and shaping global supply chains. This dominance is the result of a confluence of factors, including strategic government policies, a vast and adaptable workforce, and significant investments in infrastructure.
Understanding China’s manufacturing landscape is crucial for navigating the complexities of global trade and economics.
So you’re interested in China’s manufacturing dominance? That’s a huge topic! Check out this insightful Hacker News discussion on the subject: China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. It’s a great place to start learning about the complexities and implications of China’s position as the world’s factory. The discussion on China’s manufacturing superpower is really worth reading.
China’s Manufacturing Evolution
China’s journey to manufacturing dominance began with gradual reforms in the late 1970s, shifting from a centrally planned economy towards a more market-oriented system. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) were established, attracting foreign investment and fostering export-oriented manufacturing. This initial phase laid the groundwork for explosive growth in the following decades. Comparing China’s growth to other manufacturing giants like the US or Japan reveals a steeper and faster ascent, fueled by its unique combination of low labor costs, access to raw materials, and government support.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking. It’s a huge topic, and understanding global trade dynamics is key, especially when considering political figures like Canada’s Pierre Poilievre, whose recent interview objectives are detailed here: Pierre Poilievre dévoile ses objectifs dans une entrevue accordée à. His policies could significantly impact how Canada interacts with China’s manufacturing might, so it’s worth checking out.
Key policy decisions, such as joining the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001, further propelled its integration into the global economy.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms Begin | Initiated market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for future manufacturing growth. | Deng Xiaoping’s leadership and the shift away from a purely planned economy. |
| 1980s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted foreign investment and spurred export-oriented manufacturing. | Rapid growth in export-processing zones like Shenzhen. |
| 2001 | China joins the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Increased access to global markets and further integrated China into the global trading system. | Significant increase in Chinese exports following WTO accession. |
| 2010s | Focus on Technological Upgrading | Shift towards higher-value manufacturing and technological innovation. | Government initiatives promoting “Made in China 2025” strategy. |
Top Sectors of Chinese Manufacturing, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
China’s manufacturing prowess is evident across diverse sectors. Five key sectors – electronics, textiles, machinery, automobiles, and construction materials – significantly contribute to its global output. These sectors boast substantial global market share, leveraging technological advancements and cost advantages. However, competition from other countries, particularly in high-tech areas, presents ongoing challenges.
| Sector | Strength | Weakness | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Large-scale production, cost competitiveness, strong supply chains. | Dependence on foreign technology in some areas, environmental concerns. | Continued growth, but facing increasing competition from other Asian nations. |
| Textiles | Established infrastructure, low labor costs, diverse product range. | Environmental impact, competition from countries with even lower labor costs. | Potential for growth in high-value, specialized textiles. |
| Machinery | Growing domestic demand, increasing technological capabilities. | Technological gap compared to advanced economies. | Strong potential for growth, particularly in automation and robotics. |
| Automobiles | Expanding domestic market, government support, increasing technological sophistication. | Competition from established global brands, reliance on foreign technology in certain components. | Significant growth potential, but needs to overcome technological hurdles. |
| Construction Materials | Large-scale infrastructure projects, readily available raw materials. | Environmental concerns related to cement production, resource depletion. | Continued growth tied to infrastructure development, but needs to address sustainability issues. |
China’s Role in Global Supply Chains

China plays a central role in global supply chains, acting as a key supplier for countless products across various industries. This dominance impacts global trade and economics significantly, creating both opportunities and challenges. Many products, from electronics and apparel to automotive parts and medical equipment, heavily rely on Chinese manufacturing.
- Advantages of relying on Chinese manufacturing: Cost-effectiveness, large-scale production capacity, readily available supply chains, access to a vast workforce.
- Disadvantages of relying on Chinese manufacturing: Geopolitical risks, potential for supply chain disruptions, concerns about labor practices and environmental impact, intellectual property concerns.
Challenges and Future Trends in Chinese Manufacturing
Despite its dominance, China’s manufacturing sector faces significant challenges. Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and technological competition are key factors impacting its future trajectory. Automation and AI are reshaping the manufacturing landscape, creating both opportunities and threats. China is actively pursuing strategies to maintain its leadership, including investing in technological innovation, upgrading its workforce skills, and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
So, that Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking. It’s crazy how much stuff they make, including components for devices like iPhones. Speaking of which, check out this article about Apple paying a hefty sum to settle a lawsuit: Apple to pay $95M to settle lawsuit accusing Siri of eavesdropping. It makes you wonder about the data security implications of all that global manufacturing and how it connects back to China’s role in the tech world.
| Scenario | Technological Advancements | Trade Policies | Economic Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continued Dominance | Rapid advancements in automation and AI, leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness. | Continued integration into global trade agreements. | Sustained economic growth, driving domestic demand. |
| Gradual Decline | Slower pace of technological innovation, leading to a loss of competitiveness in certain sectors. | Increased trade protectionism and tariffs. | Slower economic growth, impacting domestic demand. |
| Restructuring and Upgrading | Focus on high-value manufacturing and technological leadership in key sectors. | Strategic partnerships and collaborations with other countries. | Moderate economic growth, driven by innovation and value-added manufacturing. |
Geopolitical Factors and their Impact
Trade wars and geopolitical tensions significantly impact China’s manufacturing sector. Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the industry’s development and competitiveness. Comparing China’s strategies to those of other major players reveals distinct approaches to industrial policy and global engagement. For example, the US-China trade war led to disruptions in supply chains and increased costs for some businesses.
Environmental and Social Considerations
China’s manufacturing sector has faced criticism regarding its environmental impact, including pollution and resource depletion. Concerns about labor conditions and worker rights also persist. However, China is increasingly implementing initiatives aimed at improving environmental sustainability and social responsibility. This includes investments in renewable energy, stricter environmental regulations, and efforts to improve worker protections. The potential for a more sustainable and ethical manufacturing model in China hinges on the continued implementation and enforcement of these initiatives.
Closure
China’s manufacturing dominance is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant global implications. While its position as a manufacturing powerhouse is undeniable, the future trajectory depends on its ability to adapt to evolving technological advancements, navigate geopolitical complexities, and address critical environmental and social concerns. Understanding China’s manufacturing sector is crucial for anyone involved in global trade, economics, or international relations.
This exploration hopefully provides a clearer picture of this dynamic and ever-changing landscape.
Expert Answers: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
What are some examples of products heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing?
Electronics (smartphones, computers), textiles and clothing, toys, and many components for automobiles and other machinery.
How does China’s manufacturing sector impact global prices?
China’s large-scale production often leads to lower prices for many consumer goods due to economies of scale and efficient production processes.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding Chinese manufacturing?
Concerns exist regarding worker rights, environmental regulations, and the use of forced labor in certain industries.
Is China’s manufacturing dominance likely to continue indefinitely?
While China’s dominance is significant, it faces increasing competition and challenges that could alter its position in the future.